Saturday, 19 September 2015
Sunday, 30 August 2015
SharePoint 2013 Service Accounts
Component
|
Description
|
Account
|
Setup user account
|
Master administration account used to install and
initially configure the production SharePoint farms.
|
SPAdmin
|
Server farm account
|
This account is also referred to as the database
access account.
This account has the following properties:
The application pool identity for the SharePoint
Central Administration website.
The process account for the Windows SharePoint
Services Timer service.
The application pool for the service application
endpoint for the Security Token Service and the Application Discovery and
Load Balancer Service
|
SPFarm
|
Service Application Endpoint
|
This account is used as the identity for the
service application endpoint application pool for the following service
applications:
Access Services
Business Data Connectivity
Secure Store Service
Usage and Health Data Collection
User Profile Service
Visio Graphics Service
Word Automation Services
Excel Services
Managed Metadata
PerformancePoint
App Management
PowerPoint Conversion
|
SPSvcApp
|
Unattended Service
|
Used for authenticating with data sources within
the following content:
Excel Services
PerformancePoint
Visio
SQL Reporting Services
|
SPExcel
SPPerfPt
SPVisio
SS
|
Default Content Access
|
The default account for crawling content.
|
SPCrawl
|
Search Service
|
The Windows service account for the SharePoint
Server Search service.
|
SPSearch
|
User Profile Synchronization Service
|
This is the Windows service account for the User
Profile Synchronization Service.
|
SPUPSvc
|
Synchronization Connection
|
This is the account used to perform
synchronization with the remote directory service.
|
SPUPSync
|
App Management Service
|
This account permits you to install SharePoint
apps from the SharePoint Store or the App Catalog.
|
SPAppMgt
|
PowerPoint Conversion Service
|
This account converts Microsoft PowerPoint
presentations into various formats.
|
SPPwrPoint
|
Machine Translation service
|
This account performs automated machine
translation.
|
SPTrans
|
Access Services 2013
|
This account views, edits, and interacts with
Access 2013 databases in a browser.
|
SPAccess
|
Work Management
|
This account provides task aggregation across
work management systems, including SharePoint products, Microsoft Exchange
Server, and Microsoft Project Server.
|
SPWkMgt
|
Cache User
|
SPCacheU
|
|
Cache Reader
|
SPCacheR
|
|
Application pool identity
|
The user account that the worker processes that
service the application pool use as their process identity. This account is
used to access content databases that are associated with the web
applications that reside in the application pool.
|
SPWPDflt
|
Claims to Windows Token Service
|
This account will be used to perform Kerberos
authentication with Service Applications in the farm.
|
SPC2WTS
|
FIM Sync Account
|
This account will be used by the FIM MA to
populate the UPS with profile data.
|
SPFIMSync
|
Tuesday, 25 August 2015
Optimizing SQL for SharePoint 2013
Setting
|
Recommendation
|
Notes
|
TempDB
|
Increase its initial size. Try starting with 500
MB
Set to simple recovery mode
Set Autogrowth to use MB, not %
Autogrowth value should be larger, not smaller.
Something like 500 MB should be a good starting value.
Put on the fastest available non-system drive. If
you separate it, calculate the number of cores you have on the server
|
Use rule of 1 file/CPU core
Ensure Data files have same initial size and Autogrowth
settings!
|
Data Files
|
Use Multiple Data Files for Content and Search
DB's
Distribute Equally-Sized Data Files (.NDF) Across
Separate Disks
Number of Data Files Should Be <= Number of
Processor Cores
Multiple Data Files Not Supported for Other DB's
|
|
Auto growth settings - don't use %
|
Do not keep the default value which is 1 MB
To avoid performance issues and reduce fragmented
data files, you should set the autogrowth value to a fixed number of megabytes.
Recommendation is 1024 MB for data files and 256
MB for log files
|
- Use a fixed number of megabytes instead of to a
percentage. The bigger the database, the bigger the growth increment should
be: From <http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh292622(v=office.15).aspx>
- For a managed production system, consider autogrowth
to be merely a contingency for
unexpected growth. Do not use the autogrow option to manage your data and log
growth on a day-to-day basis. Instead, set the autogrowth to allow for an approximate size in one year
and then add a 20 percent margin for error. Also set an alert to notify you
when the database runs low on space or approaches a maximum size: From <http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh292622(v=office.15).aspx>
|
Initial DB and Log files
|
ALTER DATABASE MAXSIZE property
The initial size is the size of the Databases
when they will be created. The default is only set at 3MB. That means that
when your content Databases are created, they only take up 10MB. This means
every time you do something in SharePoint, such as a adding a document, the
Database will have to grow (more info later) before being able to write that
data. This is an operation that can be avoided by correctly setting a
Database size up front. It is a best practice to set your initial size to how
much data
you expect to have per content database in a
year. Yes, it will take more space on your disks initially, however your
performance will be far better
Furthermore, the log should be at about 25% of the database initial size
|
|
Avoid shrinking DB files
|
Set Auto Shrink to FALSE
|
Never shrink. Will increase fragmentation and,
thus, negatively impact performance
|
Set Auto-create statistics to FALSE
|
Do not enable auto-create statistics on a SQL
Server that is supporting SharePoint Server. SharePoint Server configures the
required settings upon provisioning and upgrade. Auto-create statistics can
significantly change the execution plan of a query from one instance of SQL
Server to another instance of SQL Server. Therefore, to provide consistent
support for all customers, SharePoint Server provides coded hints for
queries as needed to provide the best performance across all scenarios
|
|
Config DB Recovery Model
|
Switch the configuration database to the simple
recovery model to restrict growth of the log file
|
|
Tools for Evaluating Databases
|
DBCC CHECKDB is a good SQL transaction for
regularly evaluating SharePoint DB's. Using arguments with it is not
supported, however.
DBCC SHOWCONTIG is a good SQL transaction for
showing the level of fragmentation that a DB has.
|
|
MAXMEM
|
Leave 4GB/10% for OS
Factor in requirements of other instances
|
The Maximum Memory must be set on all SQL
instances (even those unrelated to SharePoint) on a SQL Server if it is
hosting SharePoint. This is because, even if you set the maximum on the
SharePoint instance, the other non-SharePoint instances may be set to maximum
and they may take up all the available memory
|
MINMEM
|
set it at 25% of the Max server memory for a farm
where data requested by
SharePoint changes a lot, and to 60% of the Max
server memory when the data requested by SharePoint
is almost always the same.
|
SQL Server is memory hungry – set a reasonable
minimum and maximum memory. Example: 25GB minimum and 30GB maximum. In the
rare cases that SQL Server releases the memory you don’t drop below 25GB. But
that does not mean it claims the 25GB upfront
The Minimum Memory setting keeps the memory
dedicated to SQL Server from dropping below a certain amount. You should set
this too. Just set it a couple gigs less than the Maximum Memory setting
|
MAXDOP
|
1
|
|
Fill Factor
|
80%
|
|
Maintenance plans
|
Rebuild indices daily - perform a Reorganize when
your fragmentation is between 10% and 30 % as well as a Rebuild index when
your fragmentation is above 30%.
Backup Log
|
For rebuilding indexes and checking the logical
and physical DB integrity
|
SQL Server service domain account requires read
permission on the account used to create the farm database maintenance plans
|
Configured
|
|
Transfer Logins Job
|
Configured
|
JL: not going to use the SSIS stuff, just script
the logins out and a batch file scheduled task to read them in on the other
servers
|
SQL Agent running
|
Use separate Service account (Security)
|
|
Collation
|
Not fatal - SharePoint creates the DBs using the
collation Latin1_General_CI_AS_KS_WS. In future builds for SharePoint this
collation should be used at SQL install
|
|
Instant file initialization - When SQL Server
increases the size of a file, it must first initialize the new space before
it can be used. This is a blocking operation that involves filling the new
space with empty pages (zeroes). That means, before SQL can create or auto
grow, SQL must first write the size required with zeroes, and then it can
save the data. “Instant File Initialization” - a feature that allows file allocation
requests to skip zero initialization on creation. As a result, file
allocation requests can occur instantly – no matter what the file size
|
Instant file initialization is only available if
the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER) service account has been granted
SE_MANAGE_VOLUME_NAME. Members of the Windows Administrator group have this
right and can grant it to other users by adding them to the Perform Volume
Maintenance Tasks security policy. no
syntax change required – SQL Server will use it if it has access to it
|
Granting the permission "Perform Volume
Maintenance Tasks"
To use instant initialization, your SQL Server
service must be running with an account that has the required privilege. If
your SQL Server service is running as a local administrator this permission
already exists. For a service account which is not a local administrator
(again, recommended!), the necessary privilege to grant is Perform Volume
Maintenance Tasks. This permission can be granted by an administrator through
the Local Security Policy tool (Start, All Programs, Administrative Tools)
and once granted, SQL Server automatically uses instant initialization.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If this permission is given while SQL Server is running, then
SQL Server must be stopped and restarted. However, once the server is
restarted, no other syntax or permissions are needed
|
SQLIO test
|
SQL storage should meet performance criteria per
sqlio.exe
|
Planned? Post UAT
|
NTFS Cluster sizes (allocation unit sizes)
|
64K
|
Plan to change 12/11/2014
|
Defrag drives containing Content DBs
|
||
Use RAID 10
|
Use RAID 10
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
SharePoint Information Architecture Diagram
Here is the template I use for Information Architecture designs. It's built using Mindjet and I flesh the nodes out with the low level d...
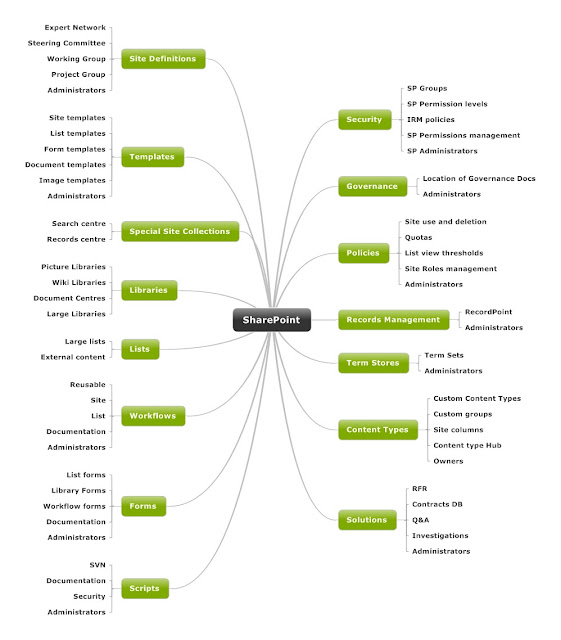
-
Introduction This document is intended to highlight possible causes of poor indexing performance on SharePoint 2007 farms as well as p...
-
OPEN FIREWALL PORTS 56737 AND 56738 Submitted Request to Open firewall ports 56737 and 56738 in Approval Environment to enable Office Ser...
-
Using stsadm to stop the osearch service will blat all the indexes: In command prompt try running: taskkill.exe /F /IM mssearch.exe /T ...


